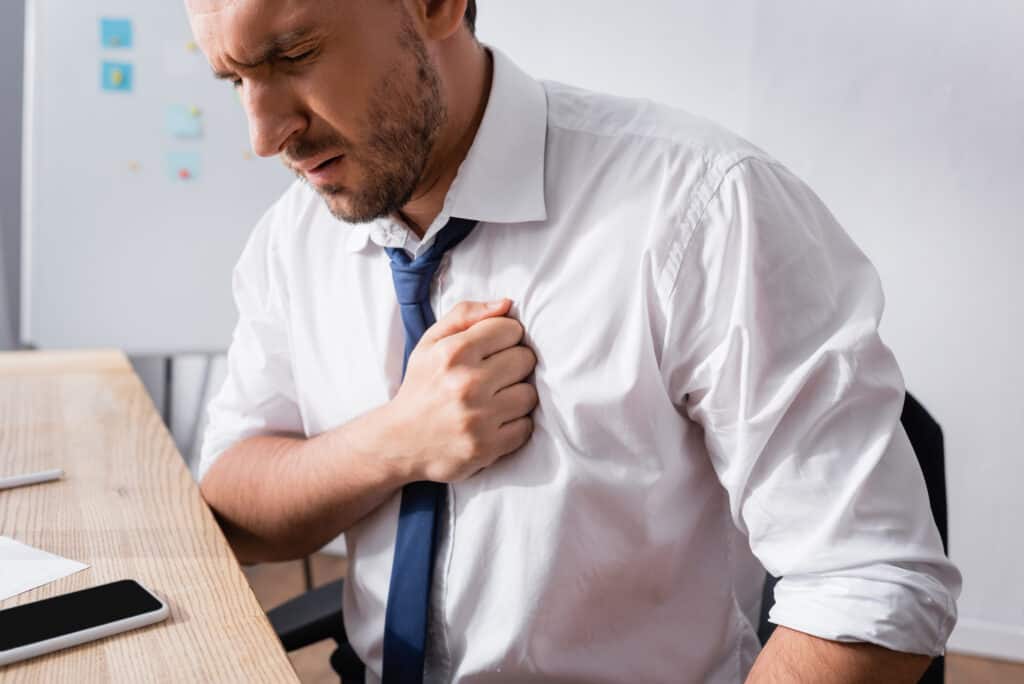
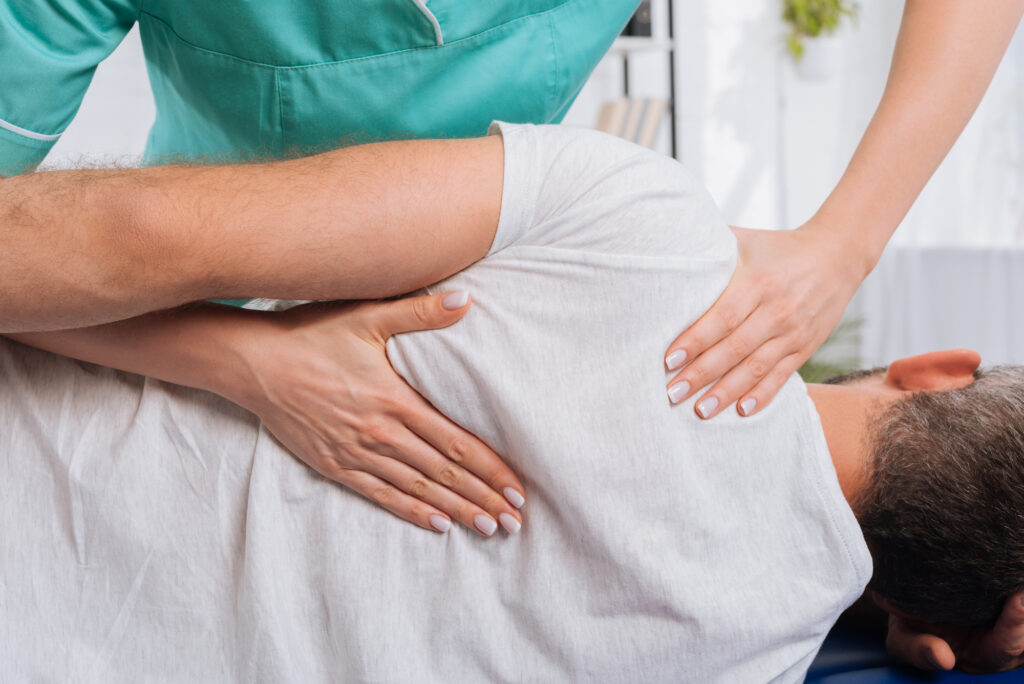
Are you experiencing chest pains and wondering if it is the result of a muscular problem or something more serious? Do you get sharp chest pains that leave you feeling worried or anxious?
If so, we understand that it can be alarming to have chest pain, whatever the cause and presentation of symptoms. Ignoring chest pain or assuming it will go away alone can have severe consequences.
So, seeking prompt medical attention can help diagnose and treat the root cause of your chest pain, enable you to experience relief, and get your life back on track. That’s why we’re here to explain what could be causing your symptoms and how best to treat them.
A pain in the chest is an incredibly common condition, affecting millions daily. While some cases may be nothing to worry about, taking your chest pains seriously and learning their causes is important.
One of the most common benign causes of chest pain is heartburn, which occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. Other potential causes of chest pains include inflammation of the muscles or cartilage between the ribs, lung problems, or even anxiety.
The pain can range from mild aching pain to severe discomfort. It can also leave you feeling uneasy, anxious, and, in some cases, panicked.
In this blog, we explore, in detail, the different types of muscle problems that can cause chest pain, such as costochondritis or rib fractures. We also discuss some helpful tips on when to seek medical attention for your chest discomfort and evaluate your options for prevention and long-term care.
So, whether you have already been diagnosed with a chest-related musculoskeletal injury or are just seeking further information, this article covers all aspects of muscular disorders and chest pain to alleviate any worries.
More Blogs From Intecore
Can High-Intensity Workouts Be Good For Overall Health?
How Can I Improve My Posture During Everyday Activities?
Shoulder Injuries That You Should Be Aware Of
What Are The Symptoms of Chest Pain?
As we already mentioned, these chest pains can be a frightening experience. However, understanding the different types of chest pain and their accompanying symptoms can help put your mind at ease. It may be helpful to journal when your chest pain occurs, how long it lasts, and what activities you are doing.
This information can help determine the cause of your chest pain. You might experience chest-related pain for many reasons, including heart disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), muscle strain, pneumonia, anxiety, and even panic attacks.
Common symptoms may include a sharp or dull sensation, tightness or burning feeling, and discomfort or pressure that spreads to the arms, jaw, or neck.
But when should you worry?
In rare cases, chest pain can be a sign of a serious, life-threatening condition like angina or a heart attack. Other times, it’s just a muscle strain. But what is the difference between muscular and cardiac chest pain?
It can be tricky to identify, as various factors can cause it. However, certain characteristics of chest pain can suggest its cause. For example, the sharp pain on one side of your chest may indicate a lung problem, such as pneumonia or a collapsed lung.
On the other hand, if the pain is accompanied by shortness of breath or a squeezing sensation, it may be a sign of a heart attack.
Chest pains can be caused by various things like musculoskeletal issues or problems with the heart. Understanding the difference is crucial in determining appropriate treatment.
- Muscular chest pain is typically caused by muscle strain or an injury to the muscles or bones in the chest wall. It may be accompanied by tenderness or aching sensations.
- On the other hand, cardiac chest pain is caused by a lack of blood flowing into the heart, often due to artery blockages. This type of pain may be described as a tightness or pressure in the chest and can also cause pain in other areas of the body, such as the arms or jaw.
Other types of chest pain include musculoskeletal pain, which may feel like a dull ache or pressure, and gastrointestinal causes like acid reflux. By paying attention to your chest pain’s location, duration, and accompanying symptoms, you can identify its cause and get the right treatment.
The important thing is – don’t try to diagnose yourself. If you are experiencing pain in your chest, you should consult a physician* if the pain feels severe and gets worse or a physical therapist if the pain is less severe to determine the underlying cause.
*If you experience chest pains lasting more than a few minutes, worsens with activity, or is accompanied by shortness of breath, you should see a physician immediately.
Additionally, chest pain accompanied by nausea, sweating, or a feeling of heartburn that doesn’t go away with antacids could be a sign of a heart attack and requires immediate medical attention.
What are Muscular Chest Pains?
Muscular or chest wall pain can result from strained muscles due to excessive exertion or repetitive movements. It may feel sharp or dull and usually occurs on one side of the chest. Managing muscular chest pains involves resting appropriately, applying heat or ice, and performing gentle stretching exercises.
Pain medications, ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can also provide relief. But the best, all-natural treatment for muscular chest pain that provides effective treatment and long-term prevention is physical therapy.
Simple self-care strategies can also ease discomfort and promote relaxation – especially if tense and tight muscles and connective tissue cause the pain. These strategies may include deep breathing exercises, gentle stretching, massage, or meditation.
Nurturing your mind and body can help you manage chest pain more effectively and improve your overall health and well-being in combination with effective physical therapy and therapeutic exercises. However, stress levels are often key to managing chest pain, as tension and anxiety can trigger muscular chest pain.
Another beneficial activity is incorporating exercise into your routine. Regular physical activity can strengthen your heart, improve circulation, and reduce stress. Additionally, making healthy dietary choices by limiting bad fats and increasing fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help decrease chest pain symptoms.
Other lifestyle modifications, including quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption, can also reduce chest pain.
How Does Physical Therapy Help With Muscular Chest Pains?
Muscular-related chest pain can indicate actual injury or damage to the area. It should be treated as soon as possible with professional physical therapy care. It can feel debilitating, especially when it affects your ability to perform daily activities.
Physical therapy can offer relief from muscular chest pain while treating any underlying conditions simultaneously. Physical therapy to treat muscular chest pain involves using exercise and movement to treat pain and improve mobility.
We target the affected muscles and help alleviate the pain. We can also help prevent future muscular chest pains by strengthening the affected muscles and improving your posture.
With our guidance, you can build strength and reduce pain without medication or surgery. From back pain to sports injuries, physical therapy is proven to be an effective way to promote healing and restore function in the body.
One of the key reasons for the effectiveness is the personalized approach we take to treating each patient. We work one-on-one with you to identify the cause of your chest discomfort and develop a customized treatment plan tailored to your needs.
This individualized approach allows us to be highly targeted and precise in application, resulting in a more effective treatment overall. We incorporate various techniques and modalities, such as exercise, manual therapy, and electrical stimulation, which all work together to address multiple aspects of your condition and promote a faster and more complete recovery.
Physical therapy is an effective, evidence-based treatment option for muscular chest pains. Through a thorough examination and evaluation, we can pinpoint the root cause of your chest pain and develop a personalized plan that may include exercises such as stretching, aerobic conditioning, and resistance training.
These exercises help increase blood flow, improve cardiovascular health, build muscular strength, and alleviate symptoms of pain and discomfort.
We can teach you a range of movement exercises to help you achieve greater strength, flexibility, and range of motion. One effective exercise is the chest press, which involves lying flat on your back with your arms extended and slowly lowering and lifting a weight to work your pectoral muscles.
Try incorporating exercises like lateral raises or front raises into your routine to target your shoulder muscles (which can also help reduce muscular chest pain). These movements involve raising your arms to the sides or directly before you while holding weights.
By incorporating various movement exercises into your workout, you can build a stronger, more flexible upper body and reduce muscular-related chest pain – for good.
- 5 Ways to Treat Chronic Back Pain Without Surgery - July 21, 2024
- 10 Back-Saving Tips for Gardening This Summer - July 14, 2024
- 5 Sciatica-Friendly Travel Tips for Your Summer Vacation - July 7, 2024